![]()
The Cowrie – SIDS Times Magazine Fall 2017 Online Edition – Back to Table of Contents
In 2014, the SIDS Accelerated Modalities for Action (SAMOA) Pathway was agreed by the international community as a blueprint for the further implementation of the sustainable development of Small Island Developing States (SIDS). One year later, the “2030 Agenda” with its17 Sustainable Development Goals was adopted by the UNGA in September 2015. The 2030 Agenda confirmed the High Level Political Forum on Sustainable Development (HLPF) as the central UN platform for the follow-up and review of the 2030 Agenda, and that the HLPF under the auspices of ECOSOC will carry out regular voluntary reviews of implementation. For SIDS, the 2030 Agenda is the main vehicle through which the Samoa Pathway can be implemented. These countries have now, begun to focus their attention on the structures and strategies that must be put in place to implement the 2030 Agenda. The Voluntary National reviews (VNRs) present an opportunity for SIDS to assess progress and challenges on the road to implementation of the 2030 Agenda. In 2016 Samoa was the first SIDS country to present its VNR. In 2017 two SIDS -Belize and Maldives presented VNRs. Following is an overview of these two presentations Belize’s “Horizon 2030: National Development Framework 2010-2030” guides long-term national development planning and establishes a set of development goals and targets for the country. To guide SDG implementation in the medium-term, Belize has adopted the “Growth and Sustainable Development Strategy (GSDS) 2016-2020”. The Strategy aims to improve quality life for all Belizeans. For this purpose, four critical success factors have been identified;
1) Optimal National Income & Investment
2) Social Cohesion Resilience
3) National Environmental, Historical and Cultural Assessment
4) Governance & Citizen Security.

Belize Structure for Implementation
Under each of these critical success factors, Belize will strengthen institutional arrangements thus ensuring that interlinkages and over laps between goals are addressed and gaps are identified. Four technical committees related to the critical success factors have been created to review, modify and approve reports from state and non- state sources on progress towards achievement of the goals. These reports are then sent to a Chief Executive Officer’s caucus along with recommendations, for onward transmission to the Prime Minister’s office. The Ministries of Economic Development and Environment and Sustainable Development provide secretariat support to the process.
Like many of the SIDS, Maldives faces significant challenges in all three dimensions of sustainable development which are exacerbated by vulnerability to climate change and internal and external shocks. The geographic insularity, dispersed population among numerous island and high transaction costs result in limited potential for economies of scale. Despite these challenges, Maldives has been successful in implementing of the Millennium Development Goals and achieved a ‘MDG plus’ status. The country made substantial progress in eradicating extreme poverty, achieving universal education and health care and protecting terrestrial and marine biodiversity. Maldives has announced the will to continue its efforts on the SDGs by building on the successes of the MDGS and to focus efforts where progress has been slower such as empowering women, strengthening mechanisms of governance and justice, minimizing economic disparity and sustainable consumption and production to ensure no Maldivian is left behind.
With regard to the institutional arrangement for the implementation of SDGS, the National Ministerial Coordination Committee, provides overall policy guidance and political support. The Ministerial Committee is supported by a Technical Committee on SDGs, which brings together experts from various government institutions and civil society. The two committees together ensure country ownership and broad participation that will be critical for the successful implementation of SDGs. The SDGs Division at the Ministry of Environment and Energy coordinates work related to the implementation of SDGs including monitoring, reporting and follow-up on the implementation process.
Maldives has made a total of nine voluntary commitments as lead entity during the Ocean Conference.
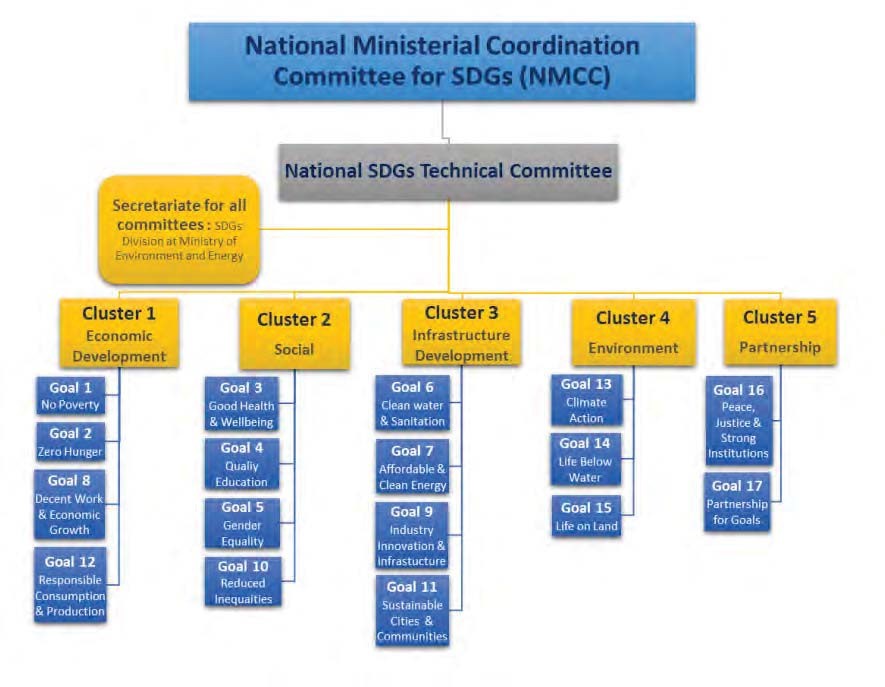
Coordination for Implementation in the Maldives
The voluntary commitments cover various topics covered during the Ocean Conference and targets of SDG 14, such as and “Introduce legal framework to reduce plastic pollution”, “Scaling up the Marine Conservation fund launched on October 2015- Improving marine scientific research and safeguarding marine resources of the Maldives through sustainable harvest”, “Avoid and Intercept ocean plastics by the fisheries industry of the Maldives”, “Implementation of strengthened and coordinated Monitoring, Control and Surveillance scheme to prevent, deter and eliminate IUU fishing” made by Ministry of Fisheries and Agriculture
Both Belize and Maldives recognized the importance of an inclusive and participatory approach by involving of different stakeholders in the implementation of SDGS which also contributes to awareness-raising. During the presentations as well as in the reports, it was demonstrated that preparations for VNRs at the national level had mobilized various stakeholders from governments, private sector, CSO, academia, scientists and other stakeholders to generate the momentum for implementation. Furthermore, this process assists countries to identify gaps, challenges and support planning process at the national level which is important also in regards to partnerships with development partners to prioritize areas for support. Considering all these, it is strongly recommended that more SIDS present VNRs to make known to the international community of the efforts and progress SIDS are making as well as define areas where support is necessary from national and international development partners. Next year seven more SIDS, Singapore, Jamaica, Cabo Verde, Dominican Republic, Kiribati and Bahamas has announced their plans to present and more is encouraged in the future HLPFs.